Major Achievements and Future Prospects of Plant Breeding
Major Achievements of Plant Breeding:-
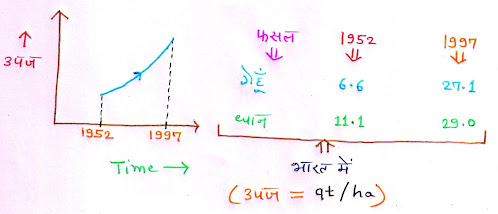
1. उपज में सुधार (Improvement in Yield):- 20वीं शताब्दी में विश्व ने सभी मुख्य फसलों की उपज में सतत बढ़ौतरी देखी। उपज में 5 से 6 गुना की वृद्धि हुई। भारत में 1952 से 1997 तक गेहूं की उपज 6.6 से बढ़कर 27.1 क्विंटल प्रति हेक्टेयर हो गयी थी तथा धान की उपज 11.1 से बढ़कर 29 क्विंटल प्रति हेक्टेयर हो गयी थी। जैसा कि नीचे diagram में प्रदर्शित किया गया है।
(The world saw a continuous increase in the yield of all major crops in the 20th century. The yield increased by 5 to 6 times. In India, the yield of wheat had increased from 6.6 to 27.1 quintal per hectare and the yield of paddy from 11.1 to 29 quintal per hectare from 1952 to 1997. As shown in the diagram below.)
2. गुणवत्ता में सुधार (Improvement in Quality):-
i. खेसारी दाल (Lathyrus sativus):- इसके के बीजों में एक न्यूरोटॉक्सिन होता है जो मानव स्वास्थ्य पर विषैला प्रभाव डालता है। इसके प्रभाव से टांगों का लकवा हो जाता है जिसे Lathyrism कहते हैं। IARI के द्वारा खेसारी दाल की नयी किस्म विकसित की गयी जिसके बीज न्यूरोटॉक्सिन रहित थे।
(Its seeds contain a neurotoxin which has toxic effects on human health. With this effect, the legs become paralyzed which is called Lathyrism. A new variety of Khesari dal was developed by IARI whose seeds were free of neurotoxins.)
ii. कपास (Cotton):- अच्छे कपास तन्तु देने वाली किस्में विकसित कर ली गयी हैं।
(Cotton varieties giving good quality fibers have been developed.)
iii. गन्ना व चुकंदर (Sugarcane and Sugar beet):- उच्च शर्करा मात्रा वाली किस्में विकसित कर ली गयी हैं।
(Varieties with high sugar content have been developed.)
iv. तेल बीज फसलें (Oil Seed Crops):- उच्च तेल मात्रा देने वाली किस्में विकसित कर ली गयी हैं।
(Varieties giving high oil content have been developed.)
v. फल व सब्जियाँ (Fruits and Vegetables):- आकर्षक गुणों व अच्छी गुणवत्ता वाली किस्में विकसित कर ली गयी हैं।
(Attractive and good quality varieties have been developed.)
3.नई क़िस्मों का निर्माण (Creation of New Varieties):-
i. गेहूँ की अर्धबौनी किस्में (Semi-dwarf Varieties of Wheat):- N. E. Borlaug ने CIMMYT (International Center of Wheat and Maize Improvement), Mexico में गेहूँ की अर्धबोनी किस्में विकसित की। Borlaug ने जापानी किस्म Norin - 10 से dwarf जीन या Norin - जीन को निकालकर गेहूँ के जीनोम में समावेशित किया और इन अर्धबौनी किस्मों को विकसित किया। 1963 में इन किस्मों को Mexico से ICAR भारत लाया गया। इन किस्मों को भारत में सोनालिका व कल्याण सोना किस्मों के रूप में द्वितीयक पुर:स्थापन किया गया। ये किस्में निम्न लक्षण दर्शाती थी:-
(N. E. Borlaug developed semi-dwarf varieties of wheat at CIMMYT (International Center of Wheat and Maize Improvement), Mexico. Borlaug isolate the dwarf gene or Norin - gene from the Japanese variety Norin - 10 and incorporated it into the wheat genome and developed these semi-dwarf varieties. These varieties were brought to ICAR India from Mexico in 1963. These varieties were introduced as secondary in India as Sonalika and Kalyan sona varieties. These varieties exhibited the following characteristics:-)
- अधिक उपज (High Yield)
- प्रकाश असंवेदी (Photo insensitive)
- कंड प्रतिरोधी (Rust Resistance)
- छोटा व मजबूत तना (Shorter and Strong Straw)
- उच्च उर्वरक प्रतिक्रिया (High Fertilizer Responsiveness)
ii. धान की अर्धबौनी किस्में (Semi-dwarf Varieties of Paddy):- Dee – geo – woo – gen, Taching Native – 1, IR – 8.
Dee – geo – woo – gen बौनी, शीघ्र पकने वाली व जापानी धान की ताइवान किस्म थी। Taching Native – 1 व IR – 8 दोनों किस्मों को IRRI, फिलीपीन्स में विकसित किया गया था। Taching Native – 1 व IR – 8 दोनों किस्मों को 1966 में भारत लाया गया था।
ये किस्में निम्न लक्षण दर्शाती थी:-
(Dee - geo - woo - gen was dwarf, early maturing and a Taiwanese variety of Japanese paddy. Both Taching Native - 1 and IR - 8 varieties were developed at IRRI, Philippines. Both the Taching Native - 1 and IR - 8 varieties were brought to India in 1966.
These varieties exhibited the following characteristics:-)
- नहीं गिरने वाली (Lodging Resistance)
- उर्वरक प्रतिक्रियात्मक (Fertilizer Responsive)
- अधिक उपज (High Yield)
- प्रकाश असंवेदी (Photo insensitive)
iii. संकर किस्में (Hybrid Varieties):-
मक्का की संकर किस्में:- गंगा सफ़ेद – 2, दक्कन
(Hybrid varieties of maize:- Ganga safed - 2, Deccan)
ज्वार की संकर किस्में:- CSH – 1 से CSH -11
(Hybrid varieties of Sorghum:- CSH - 1 to CSH - 11)
बाजरा की संकर किस्में:- PHB – 10, PHB-14, BJ – 104, BK – 506
(Hybrid Varieties of Bajra:- PHB – 10, PHB-14, BJ – 104, BK – 506)
कपास की संकर किस्में:- H4, H6, CBS-156, AKH – 468, सुगाना
(Hybrid varieties of cotton:- H4, H6, CBS-156, AKH – 468, Sugana)
4. शीघ्र परिपक्वता (Early Maturation):- फसलों के परिपक्वन काल को कम कर दिया गया है। कपास जो पहले 270 दिन में पकती थी अब 170 दिन में पाक जाती है।
(The maturity period of crops has been reduced. Cotton which used to mature in 270 days, now mature in 170 days.)
लाभ (Benefits):-
- उत्पादकता में वृद्धि।
(Increase in productivity.)
- एक से अधिक फसलें।
(More than one crops.)
- लेट सीजन पीड़कों से बचाव।
(Protection from late season pests.)
- फसल प्रबंधन में सहायता।
(Helpful in crop management.)
- फसल खर्च व पीड़कनाशी स्प्रे में कमी।
(Crop cost and pesticide uses are reduced.)
5. जैविक व अजैविक प्रतिबल रोधिता (Biotic and Abiotic Stress Resistance):- रोग रोधिता, कीट रोधिता, सूखा रोधिता, शीत रोधिता आदि गुण फसलों में विकसित कर लिए गए हैं। जिससे इनके उत्पादन को स्थिर कर लिया गया है।
(Disease resistance, insect resistance, drought resistance, cold resistance etc. properties have been developed in crops. Due to which their production has been stabilized.)
6. गन्ने का नोबिलाईजेशन (Nobilization of Indian Sugarcane):-
गन्ना प्रजनन केंद्र, कोयम्बटूर पर भारतीय गन्ने Saccharum barberi का संकरण ऊष्ण कटिबंधीय गन्ने Saccharum officinarum से कराकर भारतीय गन्ने में सुधार किया गया। भारतीय गन्ना बहुत अधिक कठोर, बहुत कम उपज व बहुत कम रस वाला होता है जबकि उष्ण कटिबंधीय गन्ना बहुत अधिक कोमल, बहुत अधिक उपज, बहुत अधिक रस व बहुत कम रेशे वाला होता है जिसका तना मोटा व छिलका मुलायम होता है। परन्तु उष्ण कटिबंधीय गन्ना उत्तर भारतीय जलवायु में कम उपज देता है। इसलिए उष्ण कटिबंधीय गन्ने के उत्तम लक्षणों भारतीय गन्ने में स्थानांतरित करने के लिए इन दोनों के मध्य संकरण कराया गया। इसी प्रक्रिया को भारतीय गन्ने का नोबिलाइजेशन कहते हैं।
(Indian sugarcane was improved by hybridization of the Indian sugarcane Saccharum barberi with the tropical sugarcane Saccharum officinarum at the Sugarcane Breeding Center, Coimbatore . Indian sugarcane is very hard, very low yielding and very low in juice whereas tropical sugar cane is very soft, very high yielding, very high juice and very low fiber, which also has thick stem and soft peel. But tropical sugarcane gives less yield in North Indian climate. Hence, hybridization was carried out between the two to transfer the best characteristics of tropical sugarcane to Indian sugarcane. This process is called nobilization of the Indian sugarcane.)
Future Prospects of Plant Breeding:-
• 20वीं शताब्दी में कृष्य उत्पादन में 50% वृद्धि पादप प्रजनन के कारण तथा शेष 50% वृद्धि उत्पादन तकनीकों के कारण हुई थी।
(In the 20th century, 50% increase in agricultural production was due to plant breeding and the remaining 50% increase was due to production techniques.)
• विश्व की जनसंख्या लगातार बढ़ रही है। 2019 में विश्व की जनसंख्या 5.7 बिलियन थी जो 2050 तक बढ़कर 10 बिलियन हो जाएगी। भारत की जनसंख्या लगभग 1.5 मिलियन प्रति वर्ष की दर से बढ़ रही है।जबकि निम्न कारणों से कृषि क्षमता लगातार कम हो रही है:-
(The world's population is increasing continuously. The world population was 5.7 billion in 2019, which will increase to 10 billion by 2050. The population of India is increasing at the rate of about 1.5 million per year, while the agricultural potential is continuously decreasing due to the following reasons:-)
- सामाजिक व आर्थिक तंत्र में परिवर्तन
(Changes in social and economic system)
- तेजी से विघटित होती मृदा
(Rapidly decomposing soil)
- वन उन्मूलन
(Deforestation)
- रेगिस्तान का विस्तार
(Desert expansion)
- मृदा अपरदन
(Soil erosion)
- जल भराव
(Water lodging)
• इतनी अधिक जनसंख्या को भोजन की आपूर्ति करने के लिए हमें पादप प्रजनन के क्षेत्र में और अधिक सुधार करने होंगे।
(To supply food to such a large population, we have to make more improvements in the field of plant breeding.)
• इसलिए हमें अपने सभी विकल्प खुले रखने होंगे तथा भोजन के नए स्रोतों को खोजना होगा।
(So we have to keep all our options open and find new sources of food.)
• उपज व पोषण गुणवत्ता बढ़ाने के साथ साथ हमें ऐसी फ़सली किस्में विकसित करनी होंगी जो तनावपूर्ण वातावरण में भी जीवित रह सकें।
(Along with increasing yield and nutritional quality, we have to develop crop varieties that can survive in stressful environment.)
• आधुनिक आनुवांशिक अभियांत्रिकी तकनीकों को औधौगिक उद्देश्य के लिए पादप प्रजनन में उपयोग करना होगा।
(Modern genetic engineering techniques have to be used in plant breeding for industrial purposes.)
• आज जंगली जर्मप्लाज्म आसानी से उपलब्ध हो जाता है। अत: जंगली जातियों के जर्मप्लाज्म को संरक्षित करना होगा ताकि भविष्य में इसका उपयोग किया जा सके।
(Today wild germplasm becomes readily available. Therefore, the germplasm of the wild species has to be preserved so that it can be used in the future.)
• भारत में जर्मप्लाज्म एकत्रण (Germplasm collections in India):-
i. CICR, Nagpur - कपास की 6548 एंट्रीज
(6548 entries of cotton)
ii. CPCRI, Kosaragod - पौध फसलें
(Plantation crops)
iii. CPRI, Shimla - आलू (Potato)
iv. CTRI, Rajahmundry - तंबाकू (Tobacco)
v. CTRI, Thiruvananthapuram - आलू को छोड़कर शेष कंदीय फसलें
(Tuber crops except potatoes)
vi. CRRI, Cuttack - धान की 15000 से भी अधिक एंट्रीज
(More than 15000 entries of paddy)
vii. DOR, Hyderabad – तेलबीज फसलें
(Oil seed crops)
viii. DWR, Karnal - गेहूँ (Wheat)
ix. IARI, New Delhi - मक्का (Maize)
x. IGFRI, Jhansi - हरा चारा फसलें
(Fodder crops)
xi. IIHR, Bangalore - बागवानी फसलें
(Horticultural crops)
xii. IIPR, Kalyanpur, Kanpur - दालें (Pulses)
xiii. NRCG, Junagarh - मूँगफली (Groundnut)
xiv. NRCS, Hydrabad - ज्वार (Sorghum)
xv. NRCS, Indore - सोयाबीन (Soybean)
xvi. SBI, Coimbatore - गन्ने की 28,000 एंट्रीज
(28,000 entries of sugarcane)