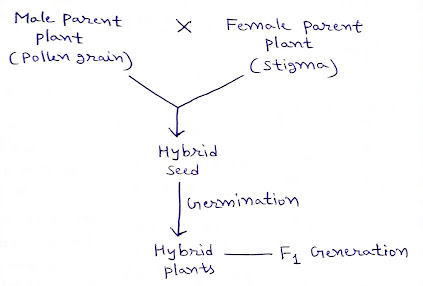
Hybridization Techniques
संकरण (Hybridization):-
दो भिन्न जीन प्रारूपों वाले व आनुवंशिक रूप से शुद्ध पौधों में से एक पौधे के परागकणों से दूसरे पौधे के पुष्पों का निषेचन करके संतति प्राप्त करने की प्रक्रिया को संकरण कहते हैं।
(Hybridization is the process of crossing two genotypically different and genetically pure plants by fertilizing flowers of one plant with pollens from other plant to obtain hybrid plant progeny.)
संकरण के 8 चरण (8 Steps of Hybridization):-
1. योजना बनाना (Planning)
2. जनकों का चयन (Selection of Parents)
3. जनकों का मूल्यांकन (Evaluation of Parents)
4. विपुंसन (Emasculation)
5. थैली लगाना (Bagging)
6. टैग लगाना (Tagging)
7. कृत्रिम परागण (Pollination)
8. F1 बीजों का एकत्रण (Collection of F1 Seeds)
1. योजना बनाना (Planning):-
• संकरण का मुख्य उद्देश्य नई किस्म का विकास करना है।
(The main objective of hybridization is to develop new varieties.)
• इस प्रक्रिया में 8-10 वर्ष का समय लग जाता है।
(This process takes 8-10 years time.)
• पादप प्रजनक को यह सुनिश्चित कर लेना चाहिए कि:-
(The plant breeder should ensure that: -)
i. किस प्रकार की किस्म का विकास करना है।
(Which kind of variety is to develop.)
ii. पुरानी किस्म के किन लक्षणों में सुधार करना है।
(Which characters of the old variety are to be improved.)
iii. कौनसे रोग व कीट रोधी जीनों का उपयोग करना है।
(Which disease and insect resistance genes are to be use.)
2. जनकों का चयन (Selection of Parents):-
• जिन लक्षणों में सुधार करना है वे लक्षण जनकों में होने चाहिए।
(The characters that are to be improved should be present in the parent plants.)
• जिस क्षेत्र के लिए किस्म तैयार करनी है उस क्षेत्र में जनक अच्छी तरह अनुकूलित होने चाहिए।
(Parent plants should be well adapted in the area for which the variety is to be developed.)
• जनकों में उच्च संयोजन क्षमता होनी चाहिए।
(Parent plants should have high combining capacity.)
3. जनकों का मूल्यांकन (Evaluation of Parents):-
• जनकों को संबन्धित क्षेत्र में 1-2 वर्षों के लिए उगाकर उनका निष्पादन (Performance) ज्ञात कर लेनी चाहिए।
(Parent plant should grow in the respective field for 1-2 years and their performance should be find out.)
• मूल्यांकन में निम्न गुणों का सूक्ष्म निरीक्षण करते हैं:-
(In the evaluation, we closely observe the following properties: -)
i. अनुकूलन (Adaptation)
ii. रोग रोधिता (Disease Resistance)
iii. कीट रोधिता (Insect Resistance)
iv. भौतिक मिश्रण (Physical Mixture)
v. संयोजन क्षमता (Combining Ability)
vi. विसंयोजन (Segregation)
4. विपुंसन (Emasculation):-
• परिभाषा:- परागकणों के परिपक्व होने से पहले परागकोषों या पुंकेसरों को किसी द्विलिंगी पुष्प से निकाल देना ही विपुंसन कहलाता है।
(Before the maturation of pollens, the removal of anthers or stamens from a bisexual flower is known as emasculation.)
• विपुंसन का मुख्य उद्देश्य स्वपरागण को रोकना है।
(The main purpose of emasculation is to prevent self-pollination.)
• विपुंसन के लिए विभिन्न फसलों में विभिन्न विधियों का उपयोग किया जाता है।
(Different methods of emasculation are used in different crops.)
5. थैली लगाना (Bagging):-
• अनियंत्रित परपरागण को रोकने के लिए थैली लगाई जाती है।
(Bagging is required to prevent uncontrolled pollination.)
• विपुंसन के तुरंत बाद पुष्प को थैली में बंद करके धागे की सहायता से पुष्पवृंत या पुष्पावली वृंत से बान्ध देते हैं।
(Immediately after the emasculation, enclose the flower in a bag and tie it to the pedicel or peduncle with the help of thread.)
• निम्न में से किसी एक थैली का उपयोग कर सकते हैं-
(You can use any one of the following bags -)
i. कागज की थैली (Paper bag)
ii. नवनीत पत्र की थैली (Butter Paper Bag)
iii. वनस्पति पार्चमेंट की थैली (Vegetable Parchment bag)
iv. महीन कपड़े की थैली (Thin Cloth bag)
6. टैग लगाना (Tagging):-
• विपुंसित पुष्प के वृंत पर कागज का एक टैग बांध देते हैं।
(A tag of paper is tied on the pedicel of the emasculated flower.)
• यह टैग 2cm X 3cm आकार का चौकोर या वृताकार टुकड़ा होता है।
(The tag is a square or circular piece of size 2cm X 3cm.)
• इस पर कार्बन पेंसिल से निम्न सूचना नोट की जाती है:-
(On this, the following information is noted with a carbon pencil: -)
i. विपुंसन की तिथि (Date of Emasculation)
ii. परागण कि तिथि (Date of Pollination)
iii. नर व मादा जनकों के नाम (मादा X नर)
[Names of male and female parents (female X male)]
7. कृत्रिम परागण (Pollination):-
• नर जनक के परिपक्व व उर्वर परागकणों को विपुंसित मादा पुष्पों के वर्तिकाग्र तक पहुंचाने की प्रक्रिया को परागण कहते है।
(Pollination is the process of transporting mature and fertile pollens of male parent to the stigma of emasculated female flowers.)
• विपुंसन के अगले दिन प्रात:काल 7:30 से 10:00 बजे के मध्य परागण किया जाता है।
(Pollination is done between 7:30 am to 10:00 am on the next day of emasculation.)
• विभिन्न फसलों में परागण की विधि परिवर्तित होती रहती है। जैसे:-
(The method of pollination varies in different crops. like:-)
i. मक्का व बाजरा में परागकणों को मादा पुष्पक्रम पर छिड़कते हैं।
(In maize and pearl millet, pollens are dusted on the female inflorescence.)
ii. कपास व भिण्डी में परागकणों को ब्रुश द्वारा वर्तिकाग्र पर डालते हैं।
(In cotton and okra, pollen is transferred on to the stigma with the help of a brush.)
iii. जौं व गेहूँ में फटने वाले परागकोषों को स्पाइकिकाओं में डालते हैं।
(In barley and wheat, the bursting anthers are inserted into spikelets.)
8. F1 बीजों का एकत्रण (Collection of F1 Seeds):-
• संकरण से उत्पन्न बीजों को अलग एकत्रित करके सूखा लेते हैं।
(Seeds produced by hybridization are collected separately and dried.)
• भंडारण के लिए इनमें कोई उपयुक्त कीटनाशी मिला देना चाहिये, जिससे इनमें कीड़े न लगें।
(Some suitable insecticides should be added for storage, so that they do not get infected by insects.)
• F1 बीजों को टैगों के साथ रखना चाहिए।
(F1 seeds should be placed with tags.)
• भौतिक मिश्रण से हर संभव बचाव करना चाहिए।
(Every possible protection should be taken from physical mixing.)