Composite and Synthetic Varieties
UPDATED ON:- 01-01-2024
समिश्र व संश्लिष्ट किस्में (Composite and Synthetic Varieties):-
समिश्र किस्में (Composite Varieties):-
• परिभाषा (Definition):- जब एक से अधिक उत्कृष्ट अंत: प्रजातों का आपस में सभी संभव संयोजनों में संकरण कराकर समान मात्रा में बीजों को मिश्रित कर लिया जाता है तो इसे प्रकार बनी किस्म को समिश्र किस्म कहते हैं।
(When more than one superior inbreds are crossed in all possible combinations and equal amount of seeds are mixed together, it is called a composite variety.)
• उदाहरण (Example):-
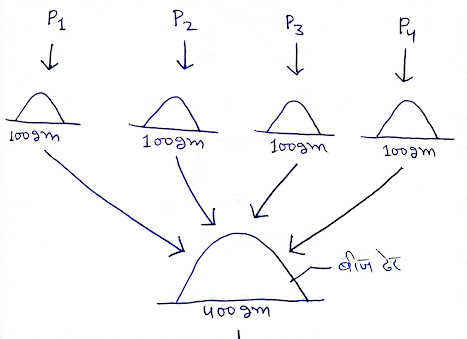
Ø माना हमारे पास 4 उत्कृष्ट अंत:प्रजात हैं – 1, 2, 3, 4
(Suppose we have 4 superior inbreds - 1, 2, 3, 4)
Ø संकरण के 6 संभव संयोजन बनते हैं -
(6 possible combinations of hybridization are made -)
विकास की विधि (Method of Development):- 3 मुख्य चरण हैं:-
(There are 3 steps:-)
a. जनकों के लिए पुनरावर्तित उपज परीक्षण (Replicated Yield Trials for parents)
b. समिश्र किस्म का निर्माण (Development of composite variety)
c. गुणन व अनुरक्षण (Multiplication and Maintenance)
a. जनकों के लिए पुनरावर्तित उपज परीक्षण (Replicated Yield Trials for parents):-
• अंत:प्रजातों के निष्पादन का पता लगाने के लिए यह परीक्षण किया जाता है।
(This test is performed to detect the performance of inbreds.)
• इस चरण में विभिन्न अंत: प्रजातों का पुनरावर्तित उपज परीक्षण किया जाता है।
(Repetitive yield trials of various inbreds are done in this step.)
• उत्कृष्ट अंत:प्रजातों का वरण कर लिया जाता है। जिन्हें जनकों के रूप में उपयोग किया जाता है। जबकि निकृष्ट अंत: प्रजातों को त्याग दिया जाता है।
(Superior inbreds are selected which are used as parents. Whereas inferior inbreds are discarded.)
b. समिश्र किस्म का निर्माण (Development of composite variety):-
• समिश्र किस्म का निर्माण 2 विधियों से किया जा सकता है –
(Composite variety can be produced by 2 methods -)
i. पूर्व संकरण विधि (Pre cross method)
ii. पश्च संकरण विधि (Post cross method)
i. पूर्व संकरण विधि (Pre cross method):-
Ø वरित अंत:प्रजात जनकों में सभी संभव संयोजनों में संकरण कराते हैं।
(Hybridization in all possible combinations is made in the selected inbred parents.)
Ø सभी संकरणों से समान मात्र में बीज लेकर मिश्रित कर लेते हैं।
(Take the equal amount of seeds from all crosses and mix them.)
Ø बीजों का यह मिश्रण ही समिश्र किस्म कहलाता है।
(This mixture of seeds is called the composite variety.)
ii. पश्च संकरण विधि (Post cross method):-
Ø समिश्र किस्म निर्माण के लिए सामान्यतया इसी विधि का उपयोग किया जाता है।
(This method is commonly used for the development of composite varieties.)
Ø सभी जनकों से समान मात्रा में बीज लेकर मिश्रित कर लेते हैं।
(Take the equal amount of seeds from all the parents and mix them.)
Ø अब इन बीजों को पृथककरण में उगाकर मुक्त परागण होने देते हैं जहां सभी संभव संयोजनों में संकरण हो जाते हैं।
(Now these seeds are grown in isolation and allow open pollination where hybridization occurs in all possible combinations.)
Ø सभी पौधों के बीजों को एकत्रित कर लेते हैं जो समिश्र किस्म को प्रदर्शित करते हैं।
(Collect seeds of all the plants which exhibit composite variety.)
नोट:- उपरोक्त दोनों विधियों द्वारा उत्पन्न समिश्र किस्मों का निष्पादन लगभग एक समान होता है।
(Note: - Composite varieties developed by both the above methods are nearly identical in performance.)
c. गुणन व अनुरक्षण (Multiplication and Maintenance):-
• गुणन व अनुरक्षण के लिए समिश्र किस्म के बीजों को पृथक्करण में उगाकर मुक्त परागण होने देते हैं।
(Composite variety seeds are grown in isolation for multiplication and maintenance and allow open pollination.)
• अगली पीढ़ी का बीज काफी अधिक पौधों के बीजों से प्राप्त होता है।
(Seed of the next generation is produced from significantly high number of plant seeds.)
• समिश्र किस्म की पीढ़ियाँ (Generations of Composite Variety):-
• उपज की तुलना (Comparison of Yield):-
• Comp.2 की उपज के लिए फॉर्मूला (Fromula for yield of Comp.2):-
समिश्र किस्मों के उदाहरण (Examples of Composite varieties):-
i. मक्का (Maize):-
Ø 1967 में विमोचित समिश्र किस्में (Composite varieties released in 1967) –
Amber, Jawahar, Kisan, Vikram, Sona, Vijay
Ø अन्य समिश्र किस्में (Other Composite Varieties)–
Co – 1, NLD, Renuka, Kanchan
ii. बाजरा (Bajra):- WCC – 75, RCBIC – 9, ICTP – 8203
संश्लिष्ट किस्में (Synthetic varieties):-
• परिभाषा (Definition):- जब एक से अधिक उच्च GCA वाले अंत: प्रजातों का आपस में सभी संभव संयोजनों में संकरण कराकर समान मात्रा में बीजों को मिश्रित कर लिया जाता है तो इसे प्रकार बनी किस्म को संश्लिष्ट किस्म कहते हैं।
(When more than one inbreds with high GCA are hybridized in all possible combinations and their seeds are mixed in equal amounts, it is called synthetic variety.)
• इस प्रकार यहाँ जनकों के वरण के लिए GCA परीक्षण किया जाता है।
(Thus, the GCA test is done for the selection of parents.)
• उदाहरण (Example):-
Ø माना हमारे पास 6 अंत:प्रजात हैं – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
(Suppose we have 6 inbreds - 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
Ø अब इन सभी का GCA परीक्षण करते हैं -
(Now GCA test is performed for all these inbreds -)
विकास की विधि (Method of Development):- 3 मुख्य चरण हैं:-
(There are 3 main steps:- )
a. जनकों के लिए GCA परीक्षण (GCA test for parents)
b. संश्लिष्ट किस्म का निर्माण (Development of synthetic variety)
c. गुणन व अनुरक्षण (Multiplication and Maintenance)
a. जनकों के लिए GCA परीक्षण (GCA test for parents):-
• इस चरण में विभिन्न अंत: प्रजातों का GCA परीक्षण किया जाता है।
(In this step, GCA test of various inbreds is done.)
• अंत: प्रजातों का GCA परीक्षण 2 विधियों द्वारा किया जा सकता है –
(GCA test of inbreds can be done by 2 methods -)
i. Top cross test:- यह परीक्षण उन फसलों में किया जाता है जिनमें परागण को आसानी से नियंत्रित किया जा सकता है। अधिकांश फसलों में इसका उपयोग किया जाता है।
(This test is done in crops in which pollination can be easily controlled. It is used in most of the crops.)
ii. Poly cross test:- यह परीक्षण उन फसलों में किया जाता है जिनमें परागण को नियंत्रित करना कठिन या असंभव होता है।
(This test is performed in crops in which pollination is difficult or impossible to control.)
उदाहरण (Example) – चारा घास (Fodder grass)
• उच्च GCA वाले अंत:प्रजातों का वरण कर लिया जाता है। जिन्हें जनकों के रूप में उपयोग किया जाता है।
(The inbreds with high GCA are selected which are used as parents.)
b. संश्लिष्ट किस्म का निर्माण (Development of synthetic variety):-
• संश्लिष्ट किस्म का निर्माण 2 विधियों से किया जा सकता है –
(The synthetic variety can be developed by 2 methods -)
i. पूर्व संकरण विधि (Pre cross method)
ii. पश्च संकरण विधि (Post cross method)
i. पूर्व संकरण विधि (Pre cross method):-
Ø वरित अंत:प्रजात जनकों में सभी संभव संयोजनों में संकरण कराते हैं।
(The Hybridization in all possible combinations is done in the selected inbred parents.)
Ø सभी संकरणों से समान मात्र में बीज लेकर मिश्रित कर लेते हैं।
(Take equal amount of seeds from all crosses and mix them.)
Ø बीजों का यह मिश्रण ही संश्लिष्ट किस्म कहलाता है।
(This mixture of seeds is called the synthetic variety.)
ii. पश्च संकरण विधि (Post cross method):-
Ø संश्लिष्ट किस्म निर्माण के लिए सामान्यतया इसी विधि का उपयोग किया जाता है।
(This method is commonly used for the development of synthetic varieties.)
Ø सभी जनकों से समान मात्रा में बीज लेकर मिश्रित कर लेते हैं।
(Take equal amount of seeds from all the parents and mix them.)
Ø अब इन बीजों को पृथककरण में उगाकर मुक्त परागण होने देते हैं जहां सभी संभव संयोजनों में संकरण हो जाते हैं।
(Now these seeds are grown in isolation and allow open pollination where hybridization occurs in all possible combinations.)
Ø सभी पौधों के बीजों को एकत्रित कर लेते हैं जो संश्लिष्ट किस्म को प्रदर्शित करते हैं।
(Collect the seeds of all the plants which exhibit a synthetic variety.)
नोट:- उपरोक्त दोनों विधियों द्वारा उत्पन्न संश्लिष्ट किस्मों का निष्पादन लगभग एक समान होता है।
(Note: - The performance of synthetic varieties developed by both the above methods is almost same.)
c. गुणन व अनुरक्षण (Multiplication and Maintenance):-
• गुणन व अनुरक्षण के लिए संश्लिष्ट किस्म के बीजों को पृथक्करण में उगाकर मुक्त परागण होने देते हैं।
(For multiplication and maintenance, the seeds of synthetic variety are grown in isolation and open pollination is allowed.)
• अगली पीढ़ी का बीज काफी अधिक पौधों के बीजों से प्राप्त होता है।
(Seed of the next generation is produced from significantly high number of plant seeds.)
• संश्लिष्ट किस्म की पीढ़ियाँ (Generations of Synthetic Variety):-
• उपज की तुलना (Comparison of yield):-
• Syn.2 की उपज के लिए फॉर्मूला (Formula for yield of Syn.2):-
• कुछ फसलों में संश्लिष्ट किस्म का गुणन नहीं किया जा सकता जैसे – चुकंदर। इसकी संश्लिष्ट किस्म के अनुरक्षण के लिए इसके जनकों का अनुरक्षण किया जाता है।
(In some crops, the synthetic variety cannot be multiplied such as beet root. For the maintenance of its synthetic variety, its parents are maintained.)
संश्लिष्ट किस्मों के उदाहरण (Examples of Synthetic varieties):-
i. चुकन्दर (Sugar Beet):- Plant synthetic – 3
ii. फूलगोभी (Cauliflower):- Synthetic – 3
iii. बाजरा (Bajra):- ICMS – 7703