Lecture-8 Advances in Hybrid Seed Production of Castor Crop
Advances in Hybrid Seed Production of Castor Crop:-
परिचय (Introduction):-
· स्त्रीपूर्वता पाये जाने के कारण अरंडी एक परपरागित फसल है। इसमें वायु परागण होता है।
(Castor is a cross pollinated crop due to the presence of protogyny. It show wind pollination.)
· अरंडी में Raceme पुष्पक्रम होता है।
(Raceme inflorescence occurs in castor.)
· व्यवस्था के आधार पर रैसीम 3 प्रकार के होते हैं:-
(Depending on the arrangement, there are 3 types of racemes: -)
i. प्राथमिक रैसीम (Primary raceme):- मुख्य तने के शीर्ष पर उत्पन्न होता है। इसे P अक्षर से दर्शाते हैं।
(Originates at the apex of the main stem. It is represented by the letter P.)
ii. द्वितीयक रैसीम (Secondary raceme):- मुख्य तने पर उपस्थित प्रथम शाखाओं के शीर्ष पर उत्पन्न होते हैं। इन्हें S1, S2 आदि अक्षरों से दर्शाते हैं।
(Originates at the apex of the first branches present on the main stem. They are represented by the letters S1, S2 etc.)
iii. तृतीयक रैसीम (Tertiary raceme):- प्रथम शाखाओं पर उपस्थित द्वितीयक शाखाओं के शीर्ष पर उत्पन्न होते हैं। इन्हें T1, T2, आदि अक्षरों से दर्शाते हैं।
(Originates at the apex of the second branches present on the first branches. They are represented by the letters T1, T2 etc.)
· पुष्पों के प्रकार के आधार पर इसमें 2 प्रकार के Raceme पाये जाते हैं:-
(Depending on the type of flowers, 2 types of raceme are found in castor: -)
a. द्विलिंगाश्रयी रैसीम (Monoecious raceme):- जब नर व मादा पुष्प दोनों एक ही रैसीम में उपस्थित होते हैं तो इसे द्विलिंगाश्रयी रैसीम कहते हैं। ऊपरी 30 – 50% भाग में मादा पुष्प होते हैं और नीचे के 50 – 70% भाग में नर पुष्प होते हैं।
(When both male and female flowers are present in the same raceme, then it is called monoecious raceme. The upper 30 - 50% part have female flowers and the lower 50 - 70% part have male flowers.)
Ø इस रैसीम पर वातावरण का बहुत अधिक प्रभाव पड़ता है।
(The environment has a great impact on this raceme.)
i. शीत ऋतु में मादा पुष्पों का प्रतिशत अधिक होता है।
(The percentage of female flowers is higher in winter season.)
ii. ग्रीष्म व वर्षा ऋतु में नर पुष्पों का प्रतिशत अधिक होता है।
(The percentage of male flowers is high in summer and rainy season.)
Ø इस रैसीम पर पोषण व आयु का भी प्रभाव पड़ता है।
(Nutrition and age also have an effect on this raceme.)
i. तरुण पौधों को अधिक पोषण मिलने पर मादा पुष्पों का प्रतिशत बढ़ जाता है।
(The percentage of female flowers increases when the young plants get more nutrition.)
ii. परिपक्व पौधों को कम पोषण मिलने पर नर पुष्पों का प्रतिशत बढ़ जाता है।
(The percentage of male flowers increases when mature plants receive less nutrition.)
b. पिस्टिलेट रैसीम (Pistillate raceme):- जब रैसीम में केवल मादा पुष्प पाये जाते हैं तो इसे मादा रैसीम कहते हैं।
(When only female flowers are found in a raceme, it is called as pistillate raceme.)
नोट (Note):- अरंडी का पौधा द्विलिंगाश्रयी होगा या मादा, यह जीन प्रारूप व वातावरण के द्वारा निर्धारित होता है। संकर बीज उत्पादन में द्विलिंगाश्रयी रैसीम वाले पौधों को नर जनक के रूप में तथा पिस्टिलेट रैसीम वाले पौधों को मादा जनक के रूप में उपयोग किया जाता है।
(Castor plant will be monoecious or female, it is determined by the genotype and environment. In hybrid seed production, plants with monoecious raceme are used as male parent and plants with pistillate raceme are used as female parent.)
पिस्टिलेट क्रियाविधि (Pistillate Mechanism):- अरंडी में पिस्टिलेट रैसीम वाले पौधों के निर्धारण की प्रक्रिया को पिस्टिलेट क्रियाविधि कहते हैं। इसमें 3 तंत्रों का उपयोग किया जाता है –
(In castor, the process of determination of plants with pistillate raceme is called pistillate mechanism. It uses 3 mechanisms -)
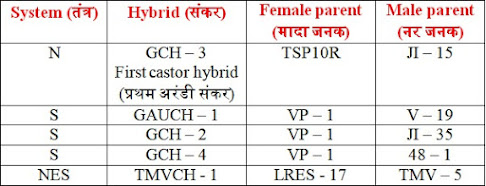
1. N type system:-
Ø इसमें जीन प्रारूप के द्वारा पिस्टिलेट वंशक्रम का निर्धारण होता है। एक अप्रभावी युग्म विकल्पी n पिस्टिलेट रैसीम निर्माण के लिए उत्तरदायी होता है।
(In this, the pistillate line is determined by genotype. A recessive allele 'n' is responsible for the formation of the pistillate raceme.)
Ø अनुरक्षण (Maintenance):-
पिस्टिलेट वंशक्रम के अनुरक्षण के लिए पिस्टिलेट पौधों का क्रॉस विषमयुग्मजी द्विलिंगाश्रयी पौधों से कराया जाता है। जिसके फलस्वरूप 50% पिस्टिलेट पौधे व 50% द्विलिंगाश्रयी पौधे प्राप्त होते हैं। संकर बीज उत्पादन के दौरान इन 50% द्विलिंगाश्रयी पौधों को पुष्पन से पहले रोगिंग करके हटा दिया जाता है।
(Pistillate plants are crossed with heterozygous monoecious plants to maintain pistillate line. As a result 50% pistillate plants and 50% monoecious plants are obtained. During hybrid seed production these 50% monoecious plants are removed before flowering.)
2. S type system:-
Ø S = Sex reversal variants
Ø इजराइल में विकसित किया गया था।
(It was developed in Israel.)
Ø एक पिस्टिलेट वंशक्रम में केवल 50 – 70% पौधे ही पिस्टिलेट होते हैं।
(Only 50 - 70% of plants are pistillate in a pistillate line.)
Ø पिस्टिलेट पौधे विकास की विभिन्न अवस्थाओं पर द्विलिंगाश्रयी पौधों में प्रत्यावर्तित हो जाते हैं।
(Pistillate plants revert to monoecious plants at different stages of development.)
i. प्रथम व द्वितीय क्रम के प्रत्यावर्तन में 30 - 40% पौधे द्विलिंगाश्रयी हो जाते हैं जिन्हें रोगिंग के द्वारा हटा दिया जाता है।
(In the first and second order reversion, 30 - 40% plants become monoecious, which are removed by rouging.)
ii. तृतीय क्रम के प्रत्यावर्तन में 10% पौधे द्विलिंगाश्रयी हो जाते हैं।
(10% plants become monoecious in third order reversion.)
Ø चूंकि बाद के प्रत्यावर्तन में 90% पौधे पिस्टिलेट होते हैं। इसलिए इन्हें संकर बीज उत्पादन में मादा जनक के रूप में उपयोग के लिए उपयुक्त माना जाता है। 10% द्विलिंगाश्रयी पौधों को पुष्पन से पहले रोगिंग करके हटा दिया जाता है।
(Since 90% plants are pistillate in the latter reversion. They are therefore considered suitable for use as female parent in hybrid seed production. 10% monoecious plants are removed by rouging before flowering.)
3. NES type system:-
Ø ये वातावरण संवेदी N – वंशक्रम होते हैं।
(These are environmental sensitive N-lines.)
Ø पुष्पन के समय तापमान पिस्टिलेट या द्विलिंगाश्रयी पौधों का निर्धारण करता है।
(The temperature at the time of flowering determines pistillate or monoecious plants.)
i. तापमान 35ºC से कम होने पर 100% पौधे पिस्टिलेट होते हैं।
(100% plants are pistillate when the temperature is below 35ºC.)
ii. तापमान 35ºC से अधिक होने पर 100% पौधे द्विलिंगाश्रयी होते हैं।
(100% plants are monoecious when the temperature is above 35ºC.)
Ø अनुरक्षण (Maintenance):- इसके लिए ग्रीष्म ऋतु में अर्थात खरीफ फसल के रूप में 300 मीटर के पृथक्करण में उगाकर गुणन करते हैं।
(For this, they are grown and multiplied as a kharif crop in the summer season in an isolation of 300 meters.)
Ø रोगिंग केवल ऑफ प्रकार के पौधों के लिए करते हैं।
(Rouging is done only for off-type plants.)
Ø यह तंत्र संकर बीज उत्पादन के लिए उपयुक्त माना जाता है।
(This mechanism is considered suitable for hybrid seed production.)
वाणिज्यिक संकर बीज उत्पादन (Commercial Hybrid Seed Production):-
Ø शीत ऋतु में अर्थात रबी फसल के रूप में अरंडी की फसल को उगाकर संकर बीज उत्पादन किया जाता है।
(In castor crop hybrid seed is produced by growing in the winter season, it means, as a rabi crop.)
Ø पृथक्करण दूरी (Isolation distance):- अरंडी की अन्य क़िस्मों व संकरों से 150 मीटर का पृथक्करण रखा जाता है।
(Isolation of 150 meters is maintained from other castor varieties and hybrids.)
Ø रोपण अनुपात (Planting Ratio):- नर व मादा जनक पौधों की पंक्तियों का अनुपात क्रमश: 1 : 3 या 1 : 4 रखा जाता है।
(The ratio of rows of male and female parent plants is kept 1: 3 or 1: 4 respectively.)
Ø नर जनक पंक्तियों को परिपक्वता से पहले ही संकर बीज खेत से हटा दिया जाता है। परिपक्वता के पश्चात मादा जनक पौधों से बीजों को एकत्रित करते हैं जो 100% संकर बीज होते हैं।
(Male parent rows are removed from the hybrid seed field before maturity. After maturation, seeds are collected from female parent plants which are 100% hybrid seeds.)
Ø निपिंग (Nipping):- इस तकनीक में अरंडी के मादा जनक पौधों की सभी कायिक कक्षस्थ कलिकाओं को हटा दिया जाता है जिससे पौधों की कायिक वृद्धि में कमी आ जाती है तथा रैसीमों की संख्या व लंबाई बढ़ने से संकर बीजों की संख्या व भार में वृद्धि हो जाती है। जिससे संकर बीज उत्पादन बढ़ जाता है।
(In this technique all the vegetative axillary buds of castor female plants are removed, which reduces the growth of the plants and increases the number and weight of the hybrid seeds by increasing the number and length of the racemes. Thereby increasing hybrid seed production.)