Cytokinins, their discovery, structure, physiological effects and applications
Cytokinin (साइटोकाइनिन):-
> It is mostly found in the roots of plants.
(यह अधिकतर पौधों की जड़ों में पाया जाता है।)
> Zeatin is the first natural cytokinin.
(Zeatin पहला प्राकृतिक साइटोकिनिन है।)
> It is biosynthesized from recycled tRNA.
(यह नवीकृत tRNA से जैवसंश्लेषित होता है।)
> Examples (उदाहरण):-
i. Kinetin (6 – Furfuryl Amino Purine)
ii. Zeatin
iii. 2 – iP (2 – Iso Pentenyladenine)
iv. BA or BAP (Benzyl Adenine or 6 – Benzyl Amino Purine)
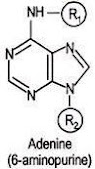
v. Adenine (Aminopurine)
1. Discovery of Cytokinins (साइटोकाइनिन की खोज):-
- Skoog, Miller and co-workers in 1955 isolate and identify kinetin, a highly-active cell division factor, from autoclaved herring sperm DNA.
(1955 में स्कूग, मिलर और सहकर्मियों ने ऑटोक्लेवित हेरिंग शुक्राणु DNA से काइनेटिन की पहचान की, जो एक अत्यधिक सक्रिय कोशिका विभाजन कारक होता है।)
- In searching for naturally occurring cytokinins in plant tissues, Letham in 1963 isolated a cytokinin, zeatin, from immature corn kernels.
(पौधे के ऊतकों में प्राकृतिक रूप से पाए जाने वाले साइटोकाइनिन की खोज में, लेथम ने 1963 में अपरिपक्व मक्के के दानों से एक साइटोकिनिन, जिआटिन को अलग किया।)
- A “kinetin-like” factor isolated by Miller in 1961 was later also identified as zeatin.
(1961 में मिलर द्वारा अलग किए गए "काइनेटिन-जैसे" कारक को बाद में जिआटिन के रूप में भी पहचाना गया।)
2. Structure of Cytokinins (साइटोकाइनिन की संरचना):- All the naturally-occurring cytokinins are substituted purines. The usual way of naming a cytokinin is to express it as a substituted 6-amino purine or as N6-substituted adenine.
(सभी प्राकृतिक रूप से पाए जाने वाले साइटोकाइनिन प्रतिस्थापित प्यूरिन्स होते हैं। साइटोकिनिन का नामकरण करने का सामान्य तरीका इसे प्रतिस्थापित 6-एमीनो प्यूरिन या N6-प्रतिस्थापित एडिनिन के रूप में व्यक्त करना है।)
i. Cell Division (कोशिका विभाजन):- Cytokinins are essential for cytokinesis though chromosome doubling can occur in their absence. In the presence of auxin, cytokinins bring about division even in permanent cells. Cell division in callus is found to require both the hormones.
(कोशिकाद्रव्य विभाजन के लिए साइटोकिनिन आवश्यक हैं, हालांकि इसकी अनुपस्थिति में गुणसूत्र द्विगुणन हो सकता है। ऑक्सिन की उपस्थिति में, साइटोकाइनिन स्थायी कोशिकाओं में भी विभाजन करते हैं। कैलस में कोशिका विभाजन के लिए दोनों हार्मोन्स की आवश्यकता होती है।)
ii. Morphogenesis (आकारिकी निर्माण):- Both auxin and cytokinins are essential for morphogenesis or differentiation of tissues and organs. Buds develop when cytokinins are in excess while roots are formed when their ratios are reversed.
(ऑक्सिन और साइटोकाइनिन दोनों आकारिकी निर्माण या ऊतकों व अंगों के विभेदन के लिए आवश्यक हैं। साइटोकाइनिन अधिक मात्रा में होने पर प्ररोह कलिकाएँ विकसित होती हैं जबकि साइटोकाइनिन कम मात्रा में होने पर जड़ें बनती हैं।)
iii. Differentiation (विभेदन):- Cytokinins induce formation of new leaves, chloroplasts in leaves, lateral shoot formation and adventitious shoot formation. They also bring about lignification and differentiation of inter-fascicular cambium.
(साइटोकाइनिन नई पत्तियों के निर्माण, पत्तियों में हरितलवक, पार्श्व प्ररोह निर्माण और अपस्थानिक प्ररोह निर्माण को प्रेरित करते हैं। ये लिग्नीकरण और अंतरा-पूलीय एधा के विभेदन को भी प्रेरित करते हैं।)
iv. Senescence (Richmond-Lang Effect) जीर्णता (रिचमण्ड लैंग प्रभाव):- Cytokinins delay the senescence of leaves and other organs by mobilisation of nutrients.
(साइटोकाइनिन पोषक तत्वों की गतिशीलता द्वारा पत्तियों और अन्य अंगों के जीर्ण होने में देरी करता है।)
v. Apical Dominance (शीर्ष प्रभाविता):- Presence of cytokinin in an area causes preferential movement of nutrients towards it. When applied to lateral buds, they help in their growth despite the presence of apical bud. They thus act antagonistically to auxin which promotes apical dominance.
(किसी क्षेत्र में साइटोकाइनिन की उपस्थिति पोषक तत्वों की इस क्षेत्र की ओर अधिक संचलन का कारण बनती है। पार्श्व कलिकाओं पर लगाने से ये शीर्षस्थ कलिका की उपस्थिति के बावजूद ये पार्श्व कलिकाओं की वृद्धि में मदद करते हैं। इस प्रकार ये ऑक्सिन के प्रति विरोधी रूप से कार्य करते हैं जो शीर्ष प्रभाविता को बढ़ावा देता है।)
vi. Seed Dormancy (बीज सुषुप्तता):- Like gibberellins, they overcome seed dormancy of various types, including red light requirement of Lettuce and Tobacco seeds.
(जिबरेलिन्स की तरह, ये विभिन्न प्रकार की बीज प्रसुप्ति को दूर करते हैं, जिसमें सलाद और तम्बाकू के बीजों की लाल प्रकाश की आवश्यकता शामिल है।)
vii. Resistance (रोधिता):- Cytokinins increase resistance to high or low temperature and disease.
(साइटोकाइनिन उच्च या निम्न तापमान और रोग के प्रति रोधक क्षमता बढ़ाते हैं।)
viii. Phloem Transport (फ्लोएम परिवहन):- They help in phloem transport.
(ये फ्लोएम परिवहन में सहायता करते हैं।)
ix. Accumulation of Salts (लवणों का जमाव):- Cytokinins induce accumulation of salts inside the cells.
(साइटोकाइनिन कोशिकाओं के अंदर लवण के संचय को प्रेरित करते हैं।)
x. Flowering (पुष्पन):- Cytokinins can replace photoperiodic requirement of flowering in certain cases.
(साइटोकाइनिन कुछ मामलों में पुष्पन की दीप्तिकालिक आवश्यकता को प्रतिस्थापित कर सकते हैं।)
xi. Sex Expression (लिंग अभिव्यक्ति):- Like auxins and ethylene, cytokinins promote femaleness in flowers.
(ऑक्सिन व एथिलीन की तरह, साइटोकाइनिन पुष्पों में मादा प्रकृति को बढ़ावा देते हैं।)
xii. Parthenocarpy (अनिषेकफलन):- Crane (1965) has reported induction of parthenocarpy through cytokinin treatment.
[क्रेन (1965) ने देखा कि साइटोकाइनिन उपचार के माध्यम से अनिषेकफलन को प्रेरित किया जा सकता है।]
xiii. Stomatal opening (रंध्रों का खुलना):- It has been shown that an increased cytokinin concentration in xylem sap promotes stomatal opening.
(यह देखा गया है कि जाइलम सैप में बढ़ी हुई साइटोकाइनिन सांद्रता रंध्र खोलने को बढ़ावा देती है।)
4. Applications of Cytokinins (साइटोकाइनिन के अनुप्रयोग):-
i. Tissue Culture (ऊत्तक संवर्धन):- Cytokinins are essential for tissue culture because besides cell division they are also involved in morphogenesis. Instead of direct addition of cytokinins, the latter may be provided to tissue culture through the addition of coconut milk or yeast extract.
(ऊत्तक संवर्धन के लिए साइटोकाइनिन आवश्यक होते हैं क्योंकि कोशिका विभाजन के अतिरिक्त ये आकारिकी निर्माण में भी शामिल होते हैं। साइटोकाइनिन को सीधे डालने की बजाय, बाद में नारियल के पानी या खमीर निष्कर्ष के माध्यम से ऊत्तक संवर्धन के लिए प्रदान किया जा सकता है।)
ii. Shelf Life (शेल्फ काल):- Application of cytokinins to marketed vegetables can keep them fresh for several days. Shelf life of cut shoots and flowers is prolonged by employing the hormones.
(बाजार में बिकने वाली सब्जियों पर साइटोकाइनिन का प्रयोग करके उन्हें कई दिनों तक ताज़ा रख सकता है। हार्मोन के प्रयोग से कटी हुई टहनियों और फूलों की शेल्फ लाइफ लंबी होती है।)
iii. Resistance (रोधिता):- Cytokinin application is helpful to plants in developing resistance to pathogens and extremes of temperature.
(साइटोकाइनिन का उपयोग पौधों को रोगजनकों और तापमान के चरम के प्रति रोधिता को विकसित करने में सहायक होता है।)
iv. Overcoming Senescence (जीर्णता से बचना):- Cytokinins delay senescence of intact plant parts.
(साइटोकाइनिन साबुत पादप भागों की जीर्णता में देरी करता है।)
.png)

Comments
Post a Comment